Data Dive: Unraveling the Wonders and
Possibilities of Big Data
Introduction
Definition:
Big data is defined as data that contains an extraordinarily large volume of complicated and unstructured data that may be analyzed or managed. It can also be defined in other ways, such as large data being data with increased variety, increasing volume, and greater velocity. This is known as three Vs.
Fig 1: Intro to Big Data
Keywords:
Complex Data: Complex data is data that contains several variables as well as relationships between those variables. In a nutshell, it is tough to comprehend.
Volume: The term "volume" refers to the amount of data or rows present in the corresponding columns, which suggests that there is a large number of data or data entries under each data subject.
Velocity: The term "velocity" refers to the rate at which data grows, which indirectly signifies the time it takes for data to grow massively.
History of big Data:
Example of Big Data:
Customer Acquisition and Retention:
In business, big data is commonly used. Any firm is entirely dependent on its clients. Customers are their primary source of income. As a result, it is critical for them to understand their customers' needs. So big data is employed in such a way that it collects or retains all data such as client details, products purchased, and recommended products. Because this is a massive volume of data, it qualifies as big data. The data is then analyzed using big data analytics, and various patterns of customers are searched, such as what all products a customer bought or was looking for, when he bought, in which month which product was searched more or bought more is the season's most popular product. As a result, the business can be improved, which equals more things sold. This type is used in Coca Cola Company.
Advertising Solutions and Marketing Insights:
Risk Management:
Risk management is the process of analyzing potential losses from corporate investments and devising proactive strategies to handle them. As many firms or companies make several investments each day, big data is employed in risk management. This is the revenue created by that company. They make a profit as well as a loss. So, utilizing big data analytics, we may examine data including numerous bank investments. Big data gives various methods for analyzing risk situations, which means that the likelihood of loss can be analyzed and an expected amount of loss projected, using which the organization can be warned and look for solutions to mitigate this loss. In this way, big data aids risk management. Risk management is the process of analyzing the amount of loss that could come from a business investment before it occurs and finding for a solution to it. However, in general, risk management in a firm entails managing or projecting a company's investment loss. The methods described above are how big data is used in risk management. UOB (United Overseas Bank Limited) in Singapore, for example, employs big data tools. It uses the term "value at risk" to describe the amount of potential losses that can result from an investment. This is known as a risk management system.
Innovations and Product Management:
Supply Chain Management:
Predict Demand: Big data analysis can help organizations detect patterns and trends in client demand, allowing them to more correctly forecast future demand. Increase Efficiency: Companies can utilize big data to track and analyze numerous parts of their supply chain, such as transportation routes, warehouse operations, and supplier performance.
Enhance Visibility: Big data enables real-time visibility into supply chain activities. Companies can monitor inventory levels, trace the movement of items, and obtain visibility into various phases of the supply chain.
Reduce Risks: Big data analysis aids in the identification of potential supply chain risks and interruptions. Companies can proactively plan for eventualities, manage risks, and maintain supply chain continuity by analyzing data on weather trends, geopolitical events, or supplier reliability.
Types of Big Data:
Structured Data:
Structured data is a type of large data in which all of the data is stored, accessed or processed in a single format that is familiar to us and straight forward to analyze.
Unstructured Data:
Unstructured data is a sort of large data in which the full data set is stored, accessed, or processed in many formats, making analysis and comprehension difficult.
Semi Structured Data:
Semi structured data is a sort of big data which contains both structured data as well as unstructured data as a part of the entire data present. It may seem to be structured but it is not perfectly structured such as the format RDBMS ( Relational Database Management System ).
Fig 3: Types of Big Data
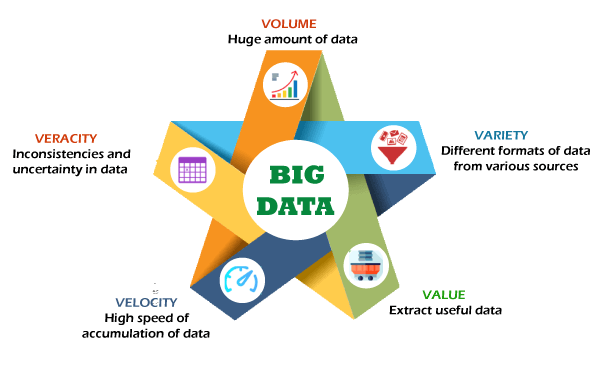
Characteristics of Big Data:
- Volume
- Velocity
- Variety
Fig 4: Characteristics of Big Data
Meticulous Observations:
- The velocity of large data is proportional to the amount of memory needed to store the big data.
- Variety in big data indicates that the data is available in a variety of formats, including audio, video, and text.
Benefits of Big Data:
Working of Big Data
Integration:
Manage:
Analyze:
After big data is managed or kept, big data analysis begins, implying that the data is meticulously scrutinized. The goal of this stage is to ensure the following:
- Better understanding of the data
- Understanding or discovering pattern trends in data for prediction
- Extracting insights from the data ( same as point 1 as better understanding of the data would help to gain information or extract information from the data ).
Fig 5: Working of Big Data
Challenges of Big Data
Quick Data Growth:
When it comes to big data, the rate of expansion can become so rapid that it becomes challenging to manage and analyze.
Storage:
When the volume of large data increases, it becomes harder to store it because all storage has a maximum size or limit.
Syncing across Data Sources:
When a large amount of data is present in several forms, the problem that occurs is that one data in one format after being imported may not be up to date when compared to other data in different formats.
Security:
When a vast volume of data is present, such as in a major firm, the data may contain valuable information that is at risk of being stolen, causing an issue for the organization.
Unreliable Data:
When such a big amount of data is present, the data may begin to contain inaccuracies as a result of the large number. Another possibility is that when such a big amount of data is present, we cannot remove the errors and outliers, which is an issue, and as a result, we cannot claim that the data is 100% correct.
Fig 6: Challenges faced by Big Data
Real Time Applications of Big Data
Big Data in Product Development:
Analyzing Customer Behaviour:
The initial stage in product development would be to take the customer's data and analyze his previous and search products to gain an understanding of the customer's conduct. Customer behaviour refers to the product they purchased and are interested in. This would allow us to better understand demand and where we could enhance sales.
Limitation:
The key issue that occurs in this step is that in order to understand the customer's behaviour, we need more data, which leads to an increase in volume data based on his search history. This would create a storage problem.
Analyzing high volume of Data Formats:
Companies must first collect data and then attempt to transform the data into a single format so that data analysis is not difficult. As a result, we would combine the data.
Limitation:
The problem that comes after integrating all of the data is that after converting all of the data into a single format, everything is mixed, making it harder to distinguish between distinct data present, therefore path analysis is required once more. As a result, we'd have more time.
Improving Customer Experience:
Big data refers to the accumulation of massive amounts of data gathered from various social media sites such as Instagram, customer feedback, and other platforms. This would allow us to learn about the interactions between customers and products, as well as the customer experience. We can deliver personalized gifts or discounts to customers depending on their conduct or experience by analyzing their behaviour or experience. This is done to keep the consumer safe. Overall, customer chunk may be regulated using this information.
Limitation:
The In Store Shopping Experience:
The corporation or business should also seek for ways to analyze geographical conditions in order to provide a pleasant in-store experience and try to provide all kinds of facilities in order to make the consumer comfortable. In addition, the corporation could consider additional solutions, such as a mobile app or website, which would simplify the customer's work and attract new customers.
Limitation:
Pricing Analytics and Optimization:
Limitation:
To perform pricing analytics, we need to have millions of transaction records saved in a database.
Fig 7: Product Development using Big Data







No comments:
Post a Comment